頸動脈斑塊內出血與臨床事件
2018-04-02 16:58:53 by admin ![]() 3296
3296
1. Symptomatic Patients With Mild and Moderate Carotid Stenosis Plaque Features at MRI and Association With Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Statin Use
中等度狹窄患者斑塊內出血發生率更高,年齡增長,斑塊內出血 幾率更高
2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque in Clinically Suspected Acute Transient Ischemic Attack and Acute Ischemic Stroke
VI型斑塊與同側急性TIA/IS發作相關,是事件發生的獨立標志特征
3. Association Between Carotid Atherosclerosis Plaque With High Signal Intensity on T1-Weighted Imaging and Subsequent Ipsilateral Ischemic Events
患有頸動脈斑塊并伴有斑塊內出血再發腦梗塞的風險更高
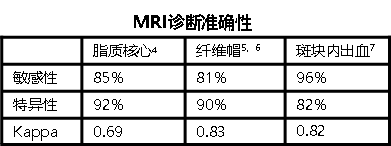
4. In vivo accuracy of multipectral magnetic resonance imaging for identifying lipid-rich necrotic cores and intraplaque hemorrhage in advanced human carotid plaques
5. Visualization of fibrous cap thickness and rupture in human atherosclerotic carotid plaque in vivo with high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging
6. In vivo accuracy of multisequence MR imaging for identifying unstable fibrous caps in advanced human carotid plaques
7. Differentiation of intraplaque versus juxtaluminal hemorrhage/thrombus in advanced human carotid atherosclerotic lesions by in vivo magnetic resonance imaging
結論:
1.斑塊內成分(出血)的出現與急性腦梗之間具有顯著相關性陰性預測值較高
2.斑塊內出血的面積及其與管腔表面的距離潛在的成為判斷急性腦梗的影像學指標
3.MRI診斷斑塊準確性

 京公網安備 11010502042883號
京公網安備 11010502042883號